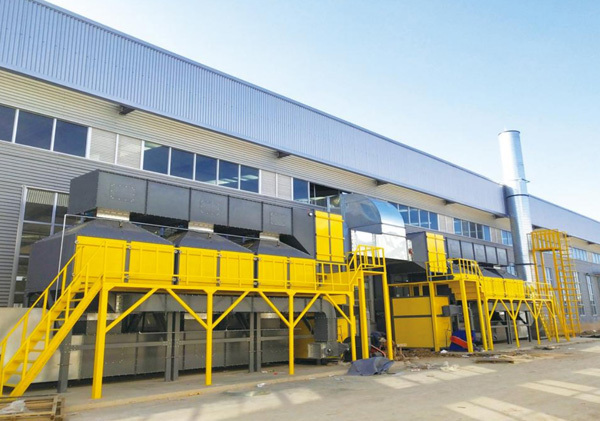



Introduction to VOCs
The main sources of volatile organic substances (VOCs) are emissions from industrial sources of pollution, and their emissions are not lower than sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, and the harm is much higher than these two pollutants. VOCs are common precursors for particle formation such as PM2.5 and ozone. The secondary gas ash formed from these make up between two-thirds and three-quarters of PM2.5 and are the main source of PM2.5.
VOCs are common precursors of particles generated by PM2.5, ozone and others, the "culprits" of fog
VOCs have low concentration, high toxicity and are known as "shadow killers"
Toxic and harmful components in VOC cause pathogenic harm to the body
The stinky components in the VOC have adverse effects on the environment and the senses
Working principle
In the chemical reaction process, the method of using a catalyst to reduce the combustion temperature and accelerate the complete oxidation of toxic and harmful gases is called catalytic combustion. Since the catalyst carrier is made of porous material, it has a large specific surface area and a suitable pore size when heated to 300 ~ At 450 °C, the organic gas passes through the catalytic layer, oxygen and organic gas are adsorbed on the catalyst in the surface layer of the porous material, which increases the likelihood of contact between oxygen and organic gas and improves activity. Which leads to a sharp chemical reaction of organic gas with oxygen to form CO2 and H2O, and also emits heat, thus the organic gas becomes a non-toxic and harmless gas.
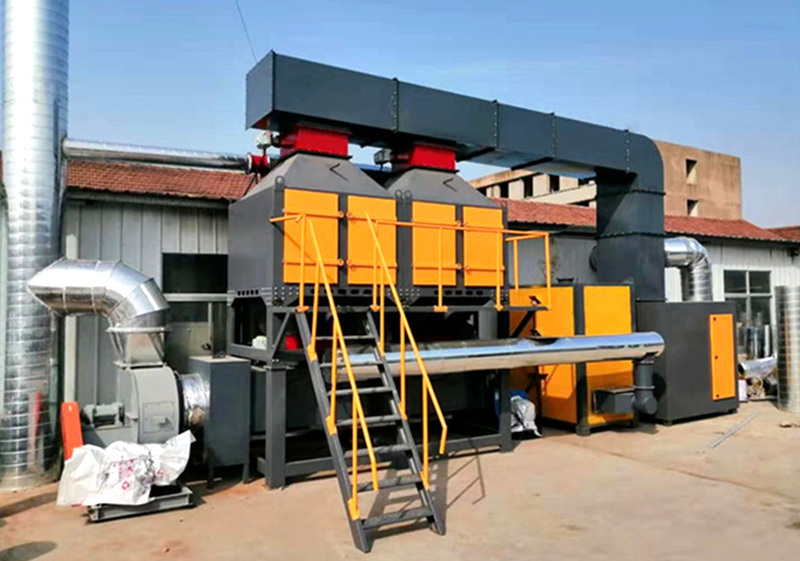
The catalytic combustion device is mainly composed of a heat exchanger, a combustion chamber, a catalytic reactor, a heat recovery system and an exhaust pipe for flue gas purification, as shown in the figure on the right.
The principle of cleaning is as follows: before entering the combustion chamber, the crude gas is preheated through a heat exchanger and directed to the combustion chamber. The required reaction temperature is achieved in the combustion chamber. The oxidation reaction is carried out in a catalytic reactor. After cleaning, the flue gas passes through the heat exchanger. Some of the heat is released and then released into the atmosphere from the chimney.
Equipment features
Convenient catalytic combustion operation, automatic control when operating the equipment. Low energy consumption, the catalytic combustion chamber uses a noble metal catalyst in the form of honeycomb ceramic as a carrier, with little resistance and high activity. When the exhaust vapor concentration reaches 2000 ppm or more, spontaneous combustion can be maintained. Safe and reliable: The equipment is equipped with fireproof and dust system, explosion-proof pressure relief system, overheating alarm system and advanced automatic control system. Low resistance and high cleaning speed. The use of modern modern cellular ceramic catalysts based on noble metals, which have a large surface area. Residual heat can be reused, waste heat can be returned to the drying channel, reducing energy consumption in the original drying tract, and can also be used as a heat source in other aspects. Small area, only 70% of similar products in the same industry ~ 80%, and there is no special equipment requirements. Long life: The catalyst is typically replaced for more than 8,000 hours and the carrier is reduced.
Processes and principles
This process mainly uses a highly efficient catalyst. The exhaust gas undergoes an oxidation reaction under the action of a catalyst to form non-toxic and tasteless carbon dioxide (CO).2And water (H)20);
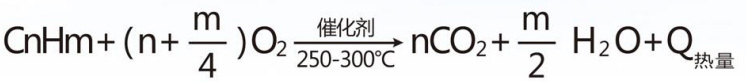
Its unique and efficient heat exchange system guarantees efficient waste heat recovery. When the exhaust gas concentration reaches a certain degree, the heat exchange system can heat the organic exhaust gases to the initial catalytic oxidation reaction temperature without electric heating, and treat the organic exhaust gases through its own thermal balance. When the temperature of the catalytic layer reaches 250-300 °C, the catalytic combustion layer begins the reaction, and the hot air produced by the exhaust gases is then used for recycling. At this time, the electric heating is stopped, outdoor heating is not required, and the service life of the ceramic honeycomb metal contained inside is 8000 hours. The whole decontamination system uses multi-point temperature control, ensure the stability of the affiliate effect.

Keywords:
Environmental
Dust Bag




Catalytic combustion equipment
Classification:











